Gibt es Nervenzellen, die für "gut" und "böse" codieren? In diesem Projekt untersuchen wir das dopaminerge und octopaminerge System der Drosophila Larve auf der Ebene einzelner Nervenzellen, um zu verstehen wie Belohnung und Bestrafung in einem Gehirnschaltkreis entsteht.
Project
Biogenic amines, especially dopamine and octopamine, serve multiple functions. This includes the processing of reward and punishment cues during associative learning. However, the question arises: Are there specialized neurons for specific brain functions?
Approach
In this project, we are investigating the anatomy and function of dopaminergic and octopaminergic cells in the brain of the Drosophila larva. Specifically, we are interested in whether there are dopaminergic and octopaminergic cells that mediate reward or punishment.
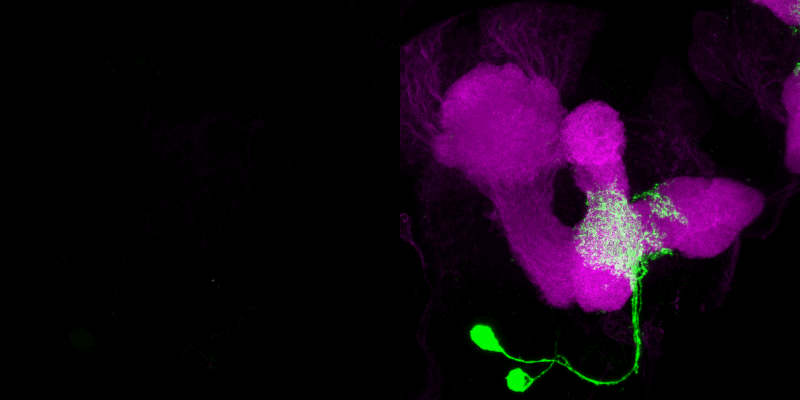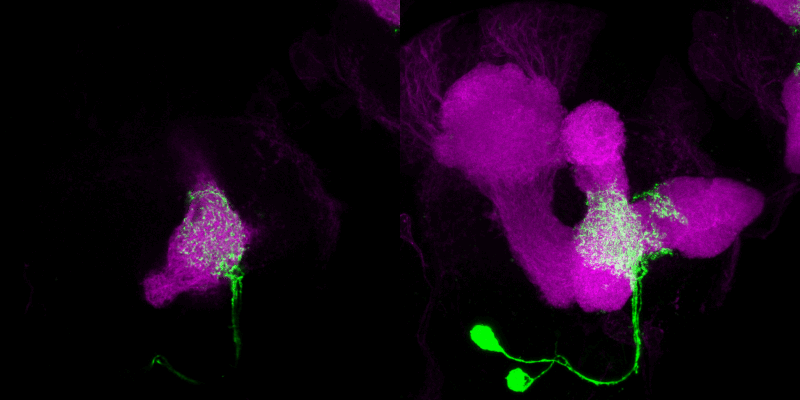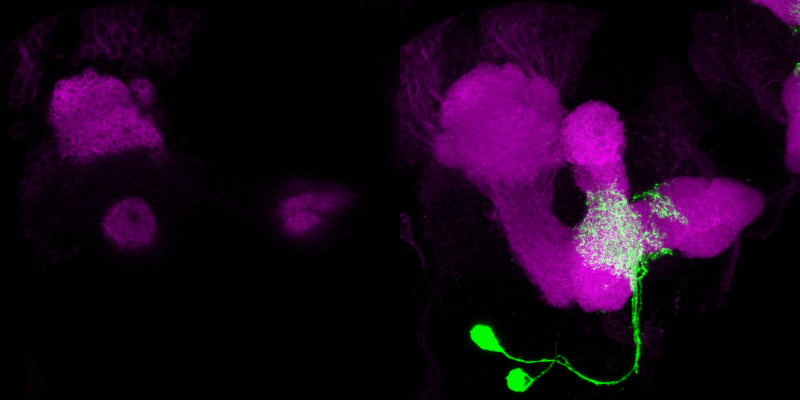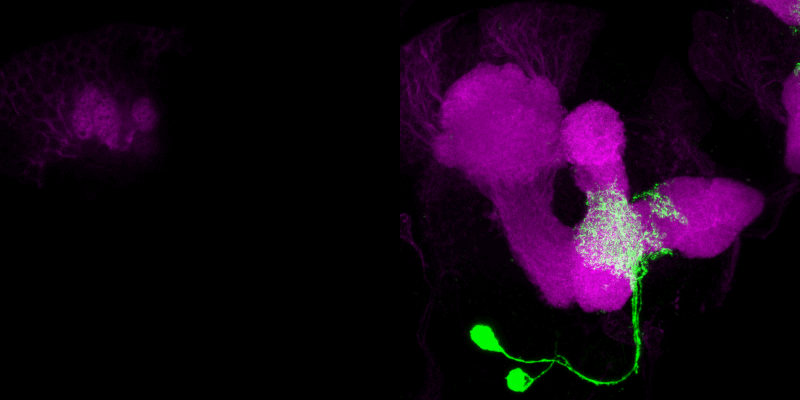
Indeed, we were able to demonstrate that only four dopaminergic cells, which divide the medial lobe of the mushroom body (a cortical brain region of higher order) into four different subunits, encode reward cues. In contrast, probably three dopaminergic neurons of the DL1 cluster mediate a punishment signal. Thus, it is reasonable to assume that there is a cellular division of labor in mediating positive and negative stimuli, an organizational principle shared between adult Drosophila and mammals.
Aim
In the medium term, this allows for analyzing how an individual dopaminergic and octopaminergic cell encodes "good" and "bad," and whether the functional mechanisms can be transferred to human medical conditions.
Publikationen
Reward signaling in a recurrent circuit of dopaminergic neurons and peptidergic Kenyon cells
Lyutova R, Selcho M, Pfeuffer M, Segebarth D, Habenstein J, Rohwedder A, Frantzmann F, Wegener C, Thum AS, Pauls D.
Nat Commun. 2019 Jul 15;10(1):3097.
DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-11092-1
Four Individually Identified Paired Dopamine Neurons Signal Reward in Larval Drosophila
Rohwedder A, Wenz NL, Stehle B, Huser A, Yamagata N, Zlatic M, Truman JW, Tanimoto H, Saumweber T, Gerber B, Thum AS.
Curr Biol. 2016 Mar 7;26(5):661-9.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2016.01.012
Characterization of the octopaminergic and tyraminergic neurons in the central brain of Drosophila larvae
Selcho M, Pauls D, Huser A, Stocker RF, Thum AS.
J Comp Neurol. 2014 Oct 15;522(15):3485-500.
DOI: 10.1002/cne.23616