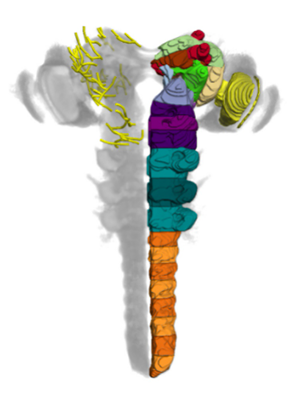
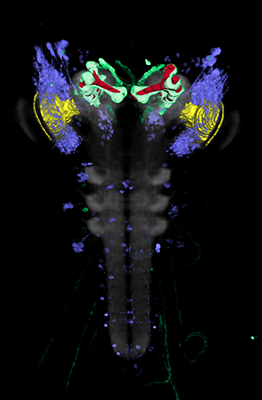
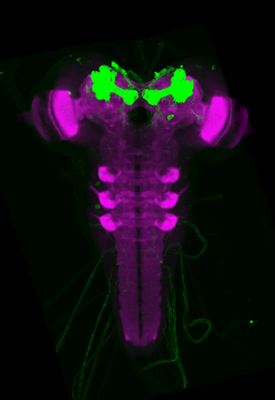
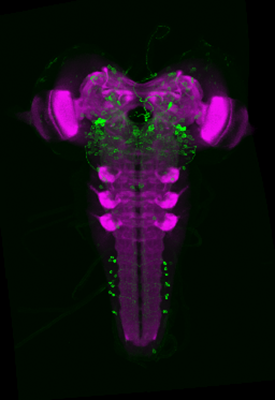
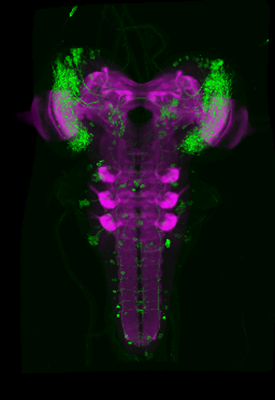
Within this project, we are developing the inaugural three-dimensional brain atlas for the Drosophila larva. This methodology not only incorporates a standardized nomenclature but also integrates several thousand genetic tools into an openly accessible online database.
Project
How does a brain organize behavior based on sensory input, motivation, or acquired experience? For centuries, this question has engaged neuroscientists from various disciplines. While it has been possible to assign certain aspects of behavior to defined brain regions, interestingly, these results are challenging to translate into models. Consequently, there is still no simple, universally accepted model for the functioning of the brain. The main challenge typically lies in the fact that the precise circuitry and connectivity of the brain, comprising thousands of neurons, are not well-known.
Approach
In this project, we have generated a standard atlas that allows the registration of existing genetic tools. This enables the visualization in 3D and searchable queries of these tools and the cells they mark within a complete larval brain.
Aim
The aim of this work is to comprehensively neuroanatomically reconstruct the brain of Drosophila during its larval development while simultaneously mapping thousands of neurogenetic tools (GAL4, LexA, Split-GAL4, ...) that allow the genetic and functional manipulation of each individual cell in the larval brain. This is a crucial step in the long-term effort to understand how the simple larval brain functions and, consequently, to identify fundamental neuronal principles that may be extrapolated to larger cellular brains in the next stage.
Publications
larvalign: Aligning Gene Expression Patterns from the Larval Brain of Drosophila melanogaster
Muenzing SEA, Strauch M, Truman JW, Bühler K, Thum AS, Merhof D.
Neuroinformatics. 2018 Jan;16(1):65-80.
DOI: 10.1007/s12021-017-9349-6